Overview
This document describes the testing of the SCI of two software applications. The first software application is for an Investment Bank and the other in Asset Management. We wanted to baseline the carbon emissions for these two software applications, to determine the data that is currently available in the organization for the calculations.
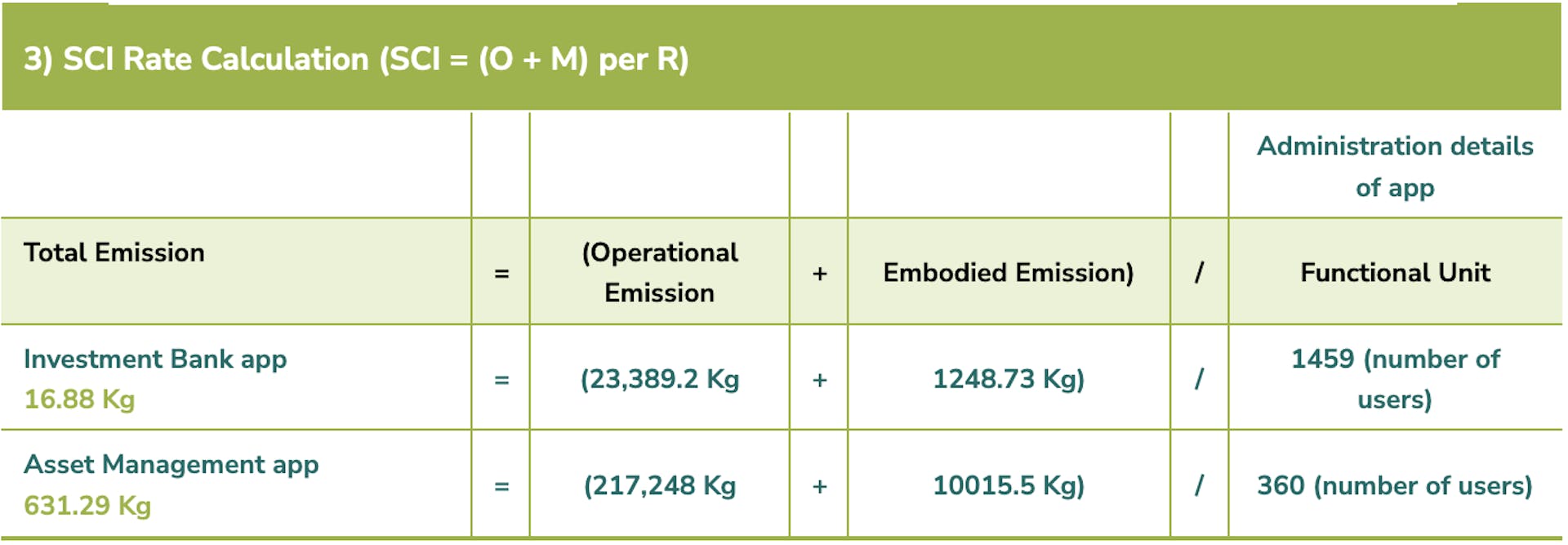
We used the SCI as defined by its specification. The SCI is a rate; carbon emissions per one unit of R (R pertains to the functional unit - per user, API call etc.).
The equation is as follows: SCI = (Operational Emissions + eMbodied Emissions) per R
The calculations do not include the embodied emissions of the rest of the computing infrastructure (e.g. the network switches, cooling equipment and other devices that power the network), which are difficult to quantify given that we do not have the necessary information regarding their distribution and usage.
Applying the SCI specification to the two use cases, involved the availability of the data for each calculation component. Where we had data within the organization we utilized, else we used data from vendors and also from publicly available energy grid metrics. We had to make assumptions to calculate the overall rate.
We recognize this is the first step in reporting the carbon emissions from our software applications and it will require further automated processes, additional data, and the ability to use the rates in order to make meaningful decisions.
Procedure
(What) Software boundary
On-prem software solution - Single scalable and reliable source of truth for reference data and metadata for research applications
On-prem software solution – Trading and order execution platform
(Scale) Functional unit
The functional unit or “R” in the SCI equation can be scaled using volumes, API calls, users etc. For the calculations for these case studies, we took "number of users". This data was collected from the application administration page where users are registered to access the associated application.
(How) Quantification method
Operational Emissions (O)
In the SCI specification, the operational emissions are calculated as:
O (Operational emissions) = ( E (Energy) * I (Location-based marginal carbon intensity) )
To calculate the total operational emissions, we also factored in virtual machine usage through the metric value “Resource Share” and the time the software is operating on the hardware per hour using the metric value “Operating Time”.
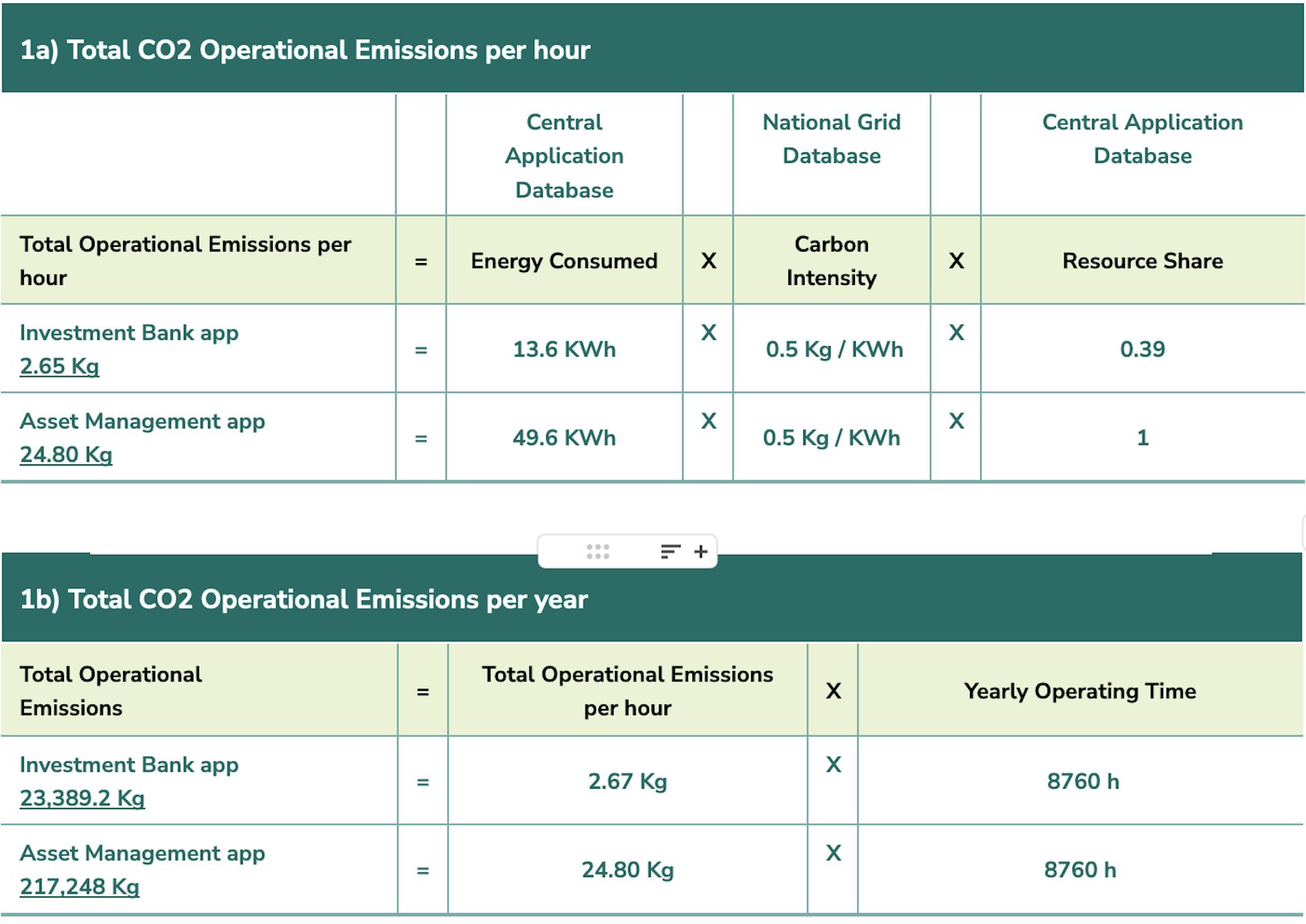
Total operational emissions = ( E (Energy) * I (Location based marginal carbon intensity) * RS (Resource share) * OT (Operating time*) )
Energy (E) – the maximum energy used by the hardware. This data is captured for all servers in the central application database.
Carbon Intensity (I) – the carbon emitted to supply 1 kWh of energy at the location of the server. This data was obtained from the national grid of the country where the data center(s) were located.
Resource Share (RS) – how much of the hardware is used by the software. This data is captured in the central application database, and for Virtual Machines the Resource Share can be derived from the hardware usage data.
Operating Time (OT) – we assumed the software is running 365 days a year, 24 hours a day. The total hours per year equates to 8760 hours. To determine the hourly operational emissions, we performed the following calculation:
Total operational emissions per hour = ( E (Energy) * I (Location based marginal carbon intensity) * RS (Resource share) )
Embodied Emissions (M)
In the SCI specification, the embodied emissions are calculated as:
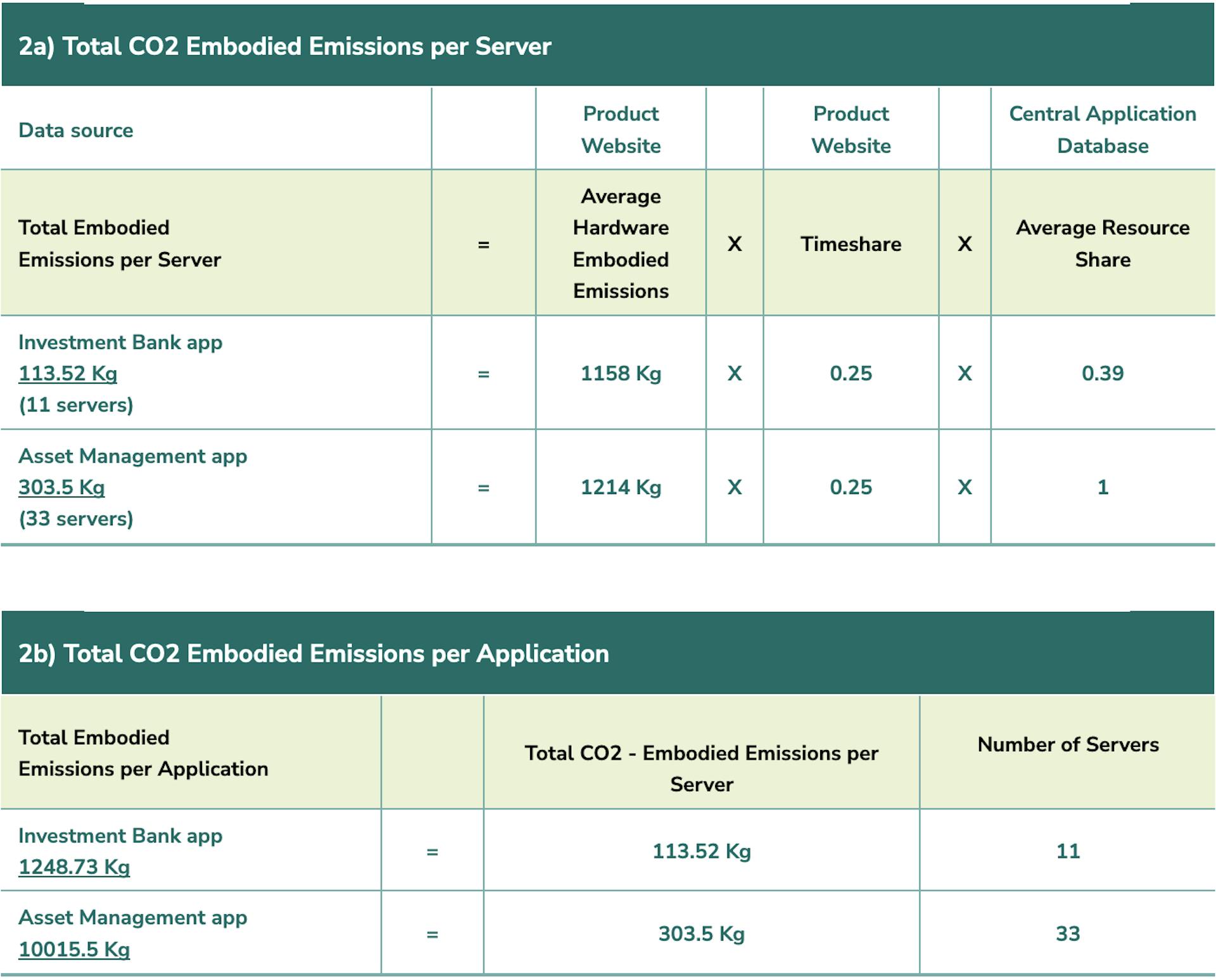
M (Embodied Emissions) = TE (Total Embodied Emissions) * TS (Time Share) * RS (Resource Share)
To calculate the total embodied emissions, we calculated individual embodied emissions using the above equation and then summed up all the servers for total embodied emissions:
Total Embodied Emissions = ∑ Embodied Emissions of Individual Servers
Total Embodied Emissions – this is the carbon footprint during the production and manufacturing of the hardware and details were taken from the manufacturer’s website (if values were available).
Time Share (TS) – the operating time of the software as a ratio of the projected hardware lifespan. The details were taken from the manufacturer’s website (if values were available).
Resource Share (RS) - how much of the hardware is used by the software. This data is captured in the central application database, and for Virtual Machines the resource share can be derived from the hardware usage data. We averaged the resource share value across the number of servers used for the application.
We removed servers that did not have associated manufacturer and specification details.
We removed servers that did not have embodied emissions from the manufacturer (note: correlation with older machines).
We assumed if the Resource Share data for software operating on a Virtual Machine is not available in the central application database, we derived the resource share by dividing the number of applications utilizing the server equally.
We assumed that the physical server is operating consistently throughout its life span as stated on the product website.
We assumed the average embodied emissions in the Total Embodied Emissions per Server calculation.
We did not factor in network energy usage.
(Quantify) SCI Value Calculation
SCI Calculations
The process of calculating the SCI rate was conducted in the following steps:
1a) Calculating the Total CO2 Operational Emissions per hour
1b) Calculating the Total CO2 Operational Emissions per year
2a) Calculating the Total CO2 Embodied Emissions per Server
2b) Calculating the Total CO2 Embodied Emissions per Application
3a) SCI Rate Calculation
This article is licenced under Creative Commons (CC BY 4.0)